Breast reconstruction
In today’s world, most women who have undergone mastectomy are eligible for breast restoration surgery. Women want breast reconstruction surgery for various reasons, some feeling incomplete and losing femininity, others simply do not like the inconvenience of external prostheses. Whatever the cause, each decision is different, and the choice of reconstructive surgery depends on the patient’s wishes and expectations.
The first and most important is to decide whether immediate restoration can take place at the same time as mastectomy, or whether only deferred breast restoration surgery can be carried out, weeks, months or even years after the tumour has been removed. It is up to the treating physician and the patient to decide together which is the right choice.
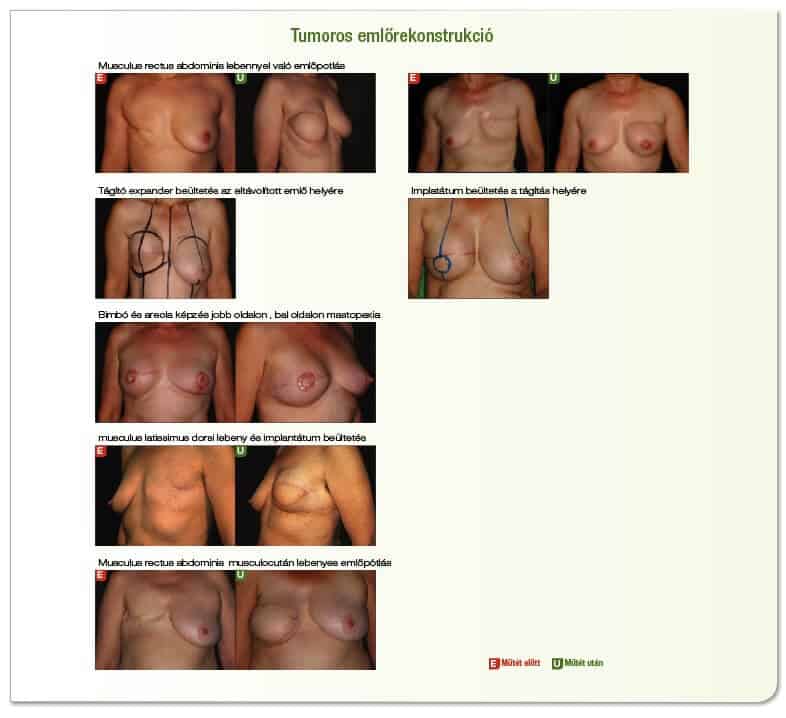
The next important choice is to select the type of reconstructive surgery. There is a wide range of procedures that can be used to replace missing breast tissue and skin using one’s own tissue or an implant or a combination of the two. The type of appropriate reconstructive surgery may depend on the method of mastectomy, the stage of the tumour, the follow-up treatment needed and the general state of health of the patient.
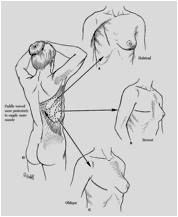
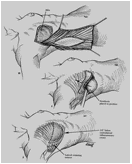
Loose replacement is a method that uses the patient’s own tissue (from the abdomen, back or bottom) to form a breast form. The transferred tissue is called loose.
The lobe is driven on the chest wall or in a tunnel under the skin, maintaining its original blood supply, or is transferred to the location of the breast removed, except from its original location, and its blood supply is ensured on the chest wall with an arsenal. Breast implants may be used in combination with any of the above techniques if the transplanted tissue cannot provide the desired relief.
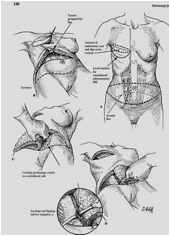
Another possible method of breast reconstruction is the use of tissue expanders and breast implants. A tissue dilator is a substance that is implanted under the skin and muscle and gradually filled with saline for several weeks to enlarge the skin. When the skin has sufficiently widened, a final implant is carried out by removing the expander in a second operation.
A second operation can be avoided by using a combined expander implant whose volume can be adapted by filling to the desired size after implantation.
It should be stressed that the surgical result must always be required for the initial damage
With regard to breast reconstruction surgery, it should be stressed that the final result will never be the same as before the breast was taken.